

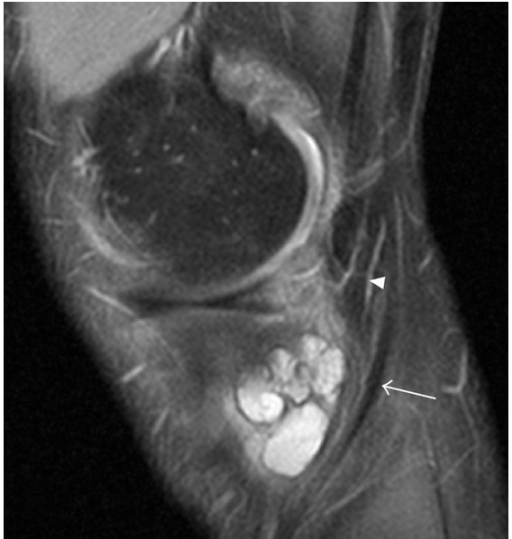
Compression: Wrapping the knee with an elastic bandage or compression stocking can help minimize the swelling and pain and support your knee.Rest: Providing ample rest to the irritated bursa to facilitate self-healing.Physical Therapy: A regular exercise regimen to improve range of motion and strengthen muscles around the knee.Ice: Application of ice packs on the inflamed bursa to decrease swelling and pain.Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that trigger symptoms and changing one’s habits.Some of the methods employed in the treatment of pes anserine bursitis include: Your doctor may order imaging studies, such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scan to rule out other problems. Fluid from your bursa may be removed for lab analysis. Pes anserine bursitis is diagnosed by reviewing your medical history and performing a thorough physical examination. Some of the common symptoms of pes anserine bursitis include: Sports requiring repetitive side-to-side motions, such as soccer and tennis.Some of the other factors that can contribute to the occurrence of pes anserine bursitis include: The condition is commonly noted in athletes, especially runners. Pes anserine bursitis mainly results from overuse or constant stress and friction on the bursa. Pain and tenderness on the inner aspect of the knee are the most common symptoms of pes anserine bursitis, also known as goosefoot bursitis. The condition occurs when the pes anserine bursa becomes inflamed and produces excess fluid causing the bursa to swell which places pressure on the adjacent sections of the knee. Pes anserine bursitis is the inflammation of the pes anserine bursa present between the tendons of the hamstring muscle and the tibia or shinbone on the inner side of the knee. A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac found between soft tissues and bones that lubricates and acts as a cushion to decrease friction between bones when they move. Bursitis refers to the inflammation and swelling of a bursa.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
